Background: Human genome studies are providing fresh insights into heart, lung, and blood (HLB) traits, with opportunities for translation of research findings to clinical and community settings for disease prevention and health promotion.
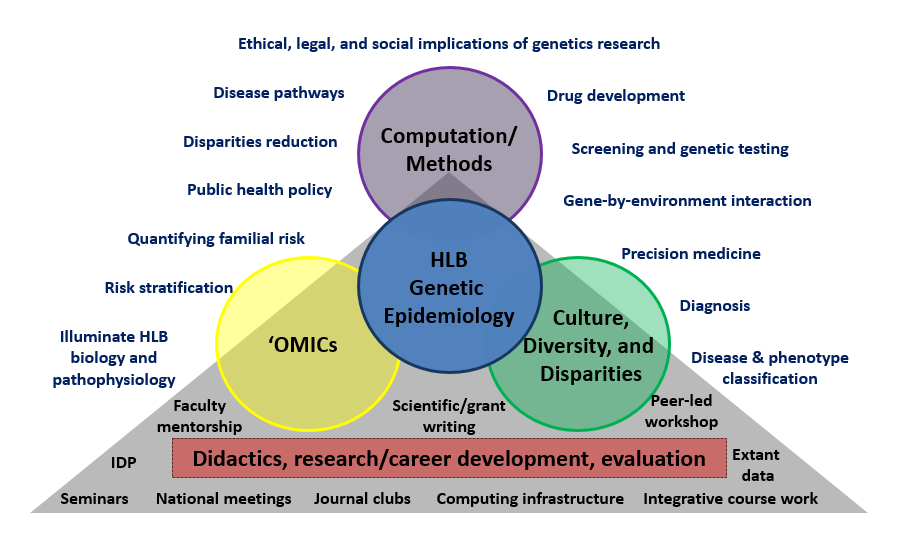
Yet, there remain an insufficient number of HLB genetic epidemiologists who can design and implement multidisciplinary HLB genetic epidemiology research that combines technological advances in genome measurement with cutting-edge statistical tools to advance understanding of the genomic basis of HLB traits and associated diseases in the most-burdened populations. The Genetic Epidemiology of Heart, Lung, and Blood Traits (or GenHLB) Training Grant responds to these research gaps by providing interdisciplinary, integrated, and comprehensive instruction in the genetic epidemiology of HLB traits from an outstanding team of research mentors with expertise spanning four proposed training dimensions: HLB genetic epidemiology; computation/methods; `OMICs; and culture, diversity, and disparities. The foundation for GenHLB training (shown in the gray triangle) supports four complementary training dimensions shown in circles. The knowledge afforded by the training surrounds the foundation and training dimensions (blue script).
Why Chapel Hill? The University of North Carolina is located in the heart of the city of Chapel Hill. As one of the three “points” of The Research Triangle in the North Carolina Piedmont, Chapel Hill, along with Raleigh and Durham, frequently receive awards for being a top location to live. Arts, entertainment, and a vibrant local food scene are significant parts of life here. In addition, Chapel Hill primary schools are routinely ranked among the nation’s best.


